What is XLH
What is XLH
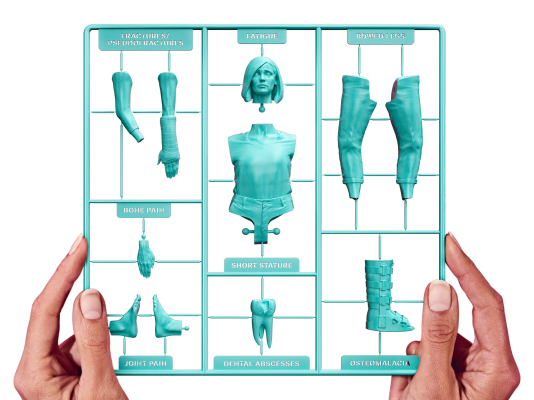
XLH is a rare, lifelong, genetic disease
Phosphorus is also found in your bones and is responsible for:

Bone growth and health

Energy for normal growth

Strengthening teeth
XLH is caused by a genetic mutation

Your doctor may refer to XLH by many different names. These include:
- X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets
- Hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets
- Familial hypophosphatemic rickets
- Vitamin D–resistant rickets (VDRR)
- Vitamin D–resistant osteomalacia
- X-linked vitamin D–resistant rickets
- Hypophosphatemic rickets
- Hypophosphatemic vitamin D–resistant rickets (HPDR)
- X-linked rickets (XLR)
- Genetic rickets
- Familial hypophosphatemia
XLH often runs in the family
If a father has XLH:
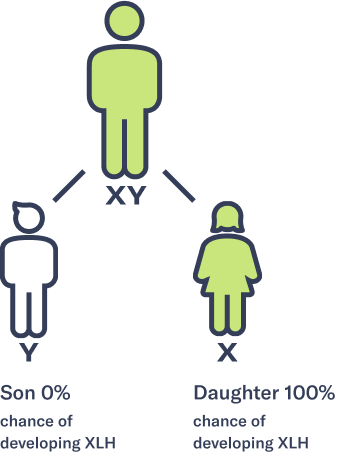
If a mother has XLH:

Did you know?
Although XLH is a hereditary condition, it can also occur spontaneously in those without any family history. About 20% to 30% of people develop XLH as a result of spontaneous mutations, which can then be passed on to their future children.
Sign up to receive helpful resources, get important event invites, and hear real patient stories that will support you on your journey.
Sign up